Table of Contents
This page provides an overview of various tools and resources for checking and selecting open source software licences and their compatibility.
Overall information and licence lists
- Software licence selection and management in GÉANT
- Important licences for licence selection
- Open Source Software Licences in GN4-3 and GN5-1 GÉANT Project: Current State and Recommendations whitepaper with a brief explanation of licence types and tables with 20 frequent licences (in GÉANT) in Appendix A
- Detailed database of licences – a set of sheets, with the first one providing an integral view of key licence characteristics
- Top open source licenses and legal risk for developers, top 20 categorised by risk, https://www.synopsys.com/blogs/software-security/top-open-source-licenses/
Mend – Open Source Licenses in 2022: Trends and Predictions, https://www.mend.io/resources/blog/open-source-licenses-trends-and-predictions/
- Standardised SPDX licence codes and licence texts, https://spdx.org/licenses/
- University of Pittsburgh Library System – Copyright and Intellectual Property Toolkit, https://pitt.libguides.com/copyright
- Mend – Open Source Licenses Explained, https://www.mend.io/resources/blog/open-source-licenses-explained/
- Free Software Foundation's free software licences and Non-free Software Licenses, classified individual licences and their compatibility with GPL, https://www.gnu.org/licenses/license-list.html
- Open Source Initiative (OSI) approved licenses
- By category, https://opensource.org/licenses/category
- Alphabetical, https://opensource.org/licenses/alphabetical
Permissive and copyleft licences
(Based on materials from ORCRO)
Permissive licences have simple requirements – to credit original work, describe changes, provide a disclaimer, etc. Copyleft licences (“reciprocal”, “protective”, “restrictive”, derogatory: “viral”) require the rights to be preserved in derivative works. If you use any components (libraries) with copyleft, you are obliged to make derived source code available, which may include the entire product/project!
- Permissive – do anything
- MIT – short and simple
- ISC (OpenBSD) – further shortened equivalent
- BSD – some versions require including the disclaimer
- Apache 2.0 – requires notice of changes, grants a license to patents unless litigating and mentions the preservation of trademark rights
- Weak copyleft – file (library) scope
- MPL 2.0 – simple, allows static linking and licence variants with additional terms
- LGPL 2.1 – cleaned text of LGPL 2.0, allows dynamic linking without enforcing copyleft
- LGPL 3.0 – grants the use of patents; the end-user must be able to install a modified version – it prohibits closed devices, DRM or hardware encryption or patents retaliation; compatible with Apache 2.0
- Strong copyleft – project scope
- GPL 2.0 – often used
- GPL 3.0 – grants the use of patents, the end-user must be able to install modified software, compatible with Apache 2.0
- AGPL 3.0 (Affero) – network protective: external use of modified(!) code requires its availability – network use is a distribution of the software, modified source code must be available
- Proprietary – these licences restrict user rights and protect the commercial interests of copyright owners
Per-feature or tabular comparisons of licences and categorised lists
- Choose an open-source license, https://choosealicense.com/appendix/
- Joinup Licensing Assistant – Find and compare software licenses, https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/collection/eupl/solution/joinup-licensing-assistant/jla-find-and-compare-software-licenses
- DejaCode licence finder; it can filter by one or several categories, licence text and a few key characteristics
- All, https://enterprise.dejacode.com/licenses/
- Permissive, https://enterprise.dejacode.com/licenses/?sort=name&category=Permissive
- Weak copyleft, https://enterprise.dejacode.com/licenses/?sort=name&category=Copyleft+Limited
- Strong copyleft, https://enterprise.dejacode.com/licenses/?sort=name&category=Copyleft
- Wikipedia tables and classified lists
- GPL-compatible licences are listed in the 'GPL (v3) compatibility' column of the table at https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_free_and_open-source_software_licences#Approvals
- Creative Commons – Can I combine material under different Creative Commons licenses in my work? https://creativecommons.org/faq/#can-i-combine-material-under-different-creative-commons-licenses-in-my-work
- The Appendix A of the whitepaper for GÉANT participants provides key characteristics of the 20 most frequently used software licences in GÉANT software projects.
Licence compatibility
GPL licences compatibility
Arrows are transitive and go from licences of the components toward the licence of your project
(From https://www.gnu.org/licenses/quick-guide-gplv3.html)
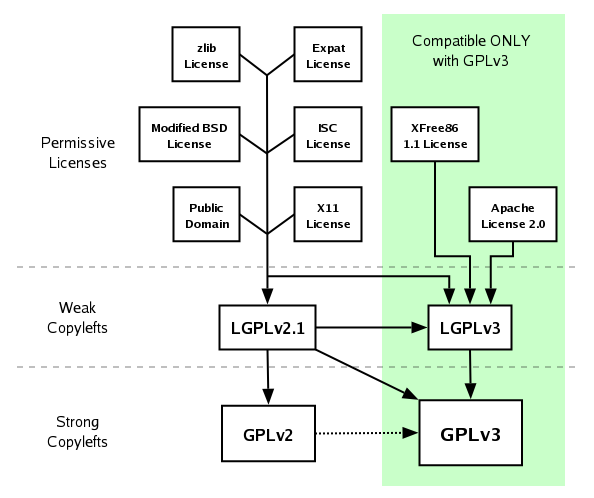
Above, per the dotted line, “GPL 2 only” is not compatible with GPL 3”, but ”GPL 2 or later” is. A more detailed view with precisely stated licences:
(From David A. Wheeler 2007, https://web.archive.org/web/20210101030518/https://dwheeler.com/essays/floss-license-slide.html, SVG variant: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/License_compatibility#/media/File:Floss-license-slide-image.svg)
On AGPL compatibility:
- (L)GPL 3.0(+) components can be used in software under AGPL, thanks to an explicit rule in GPL
- Code under AGPL cannot be used in (L)GPL projects unless dual-licensed
Relationship between most used licences in GÉANT
Following is a graph of licences that are most frequently used in GÉANT projects that were scanned using the Mend tool. It is based on the two previous graphs.
Dual and multi-licensing
- Dual and multi-licences can help avoid licence compatibility issues, making the use of components more flexible.
- You can choose a licence compatible with the one used for your software. But you cannot dual-license your software to match some components with one licence and others with another. Licences of all used components must be compatible with all of your licences.
- “Or later”(often expressed as “+”) licence variants imply the applicability of later, possibly still non-existing, versions of these licences. This is sometimes implied unless you explicitly decline it.
- Some licences include automatic relicensing (MPL 2.0, EUPL 1.2, CeCILL), while EUPL comes with a full list of licences it can be combined with.
Licence compatibility matrices or checkers
Joinup Licensing Assistant – Compatibility Checker, https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/collection/eupl/solution/joinup-licensing-assistant/jla-compatibility-checker
Licence Compatibility Checker software
In-licences (licences of components) are in rows and out-licences are in columns:
(Source: https://github.com/HansHammel/license-compatibility-checker)
Open Source Automation Development Lab (OSADL) matrix and rules
In-licences are in columns and out-licences are in rows:
(Source: Meeker, H., & von Wendorff, C. (2019). Fulfilling open source license obligations: Can checklists help?, https://events19.linuxfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/OSLS-2019-Fulfilling-Open-Source-license-obligations-Can-checklists-help.pdf)
More at
OSADL site, www.osadl.org
Open Source License Checklists Overview, https://www.osadl.org/Open-Source-License-Checklists.oss-compliance-lists.0.html
- Raw data about individual licences, https://www.osadl.org/Access-to-raw-data.oss-compliance-raw-data-access.0.html
- Matrix, https://www.osadl.org/fileadmin/checklists/matrix.html (registration needed, currently restricted to project participants)
GNU GPL licences compatibility
- Matrix of GPL and LGPL licences with detailed explanations, https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-faq.html#AllCompatibility
EUPL 1.2
Licence Compatibility, Permissivity, Reciprocity and Interoperability, general explanation and exception list approach, https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/collection/eupl/licence-compatibility-permissivity-reciprocity-and-interoperability
Matrix of EUPL compatible open source licences, what in-licences can be out-licensed under EUPL, https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/collection/eupl/matrix-eupl-compatible-open-source-licences
How to use the EUPL (What about compatibility issues?), on the use of components under EUPL with other licences, https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/collection/eupl/how-use-eupl#section-18
Creative Commons licences
Can I combine material under different Creative Commons licenses in my work? https://creativecommons.org/faq/#can-i-combine-material-under-different-creative-commons-licenses-in-my-work
Risks of licences
Risk mitigation against potentially harmful legal threats or behaviours by free-software licences
Frequently used protective and permissive licenses | |||||||
AGPLv3 | GPLv3 | GPLv2.1 | LGPLv3 | LGPLv2.1 | MPL-2 | BSD | |
Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | |
Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | |
Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No | |
Proprietization | Yes | Yes | Yes | Partial | Partial | Partial | No |
Granularity/reach | Project | Project | Project | Library | Library | File | N/A |
Trademark grant | Yes | Yes | ? | Yes | ? | No | No |
(Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Free-software_license)
Mend resources
- Understanding of licence data and compatibility in Mend, https://docs.mend.io/bundle/sca_user_guide/page/understanding_risk_score_attribution_and_license_analysis.html
- More on Mend setup assistance, Mend scan analysis and other GÉANT software review services provided by WP9T2: https://wiki.geant.org/display/GSD/Software+Reviews
Other software composition analysis (SCA, software inventory) tools
Ideally, compliance should be continuously monitored as a part of the build process.
Commercial SCA tools and services:
- The GitLab Ultimate licence compliance feature, available with the GitLab Ultimate licence and integrated into the GitLab user interface, can be integrated into GitLab-managed CI/CD pipelines, https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/compliance/license_compliance/
- FOSSA Open Source License Compliance Manager and Open Source Vulnerability Scanner, https://fossa.com/product/open-source-license-compliance
- Black Duck Software Composition Analysis, https://www.synopsys.com/software-integrity/security-testing/software-composition-analysis.html
- JFrog Xray, an add-on for Artifactory, https://jfrog.com/xray/
- Snyk, detecting and fixing code vulnerabilities, dependencies, containers, and infrastructure as code, https://snyk.io/
- Endor Labs, https://www.endorlabs.com/
OSS tools that perform SCA:
- ORT, https://github.com/oss-review-toolkit/ort
- Project in Python: Pytpip-licenses, https://pypi.org/project/pip-licenses/
- LicenseFinder from package manager data for projects in Ruby, Python, Node.js, Bower, Nuget, Golang, and Java, https://github.com/pivotal/LicenseFinder
- The SPDX SBOM Generator creates SPDX SBOMs from application package managers or build systems, https://github.com/opensbom-generator/spdx-sbom-generator
- The Tern SCA tool and Python library generate an SBOM for container images and Docker files, https://github.com/tern-tools/tern
- FOSSology, https://www.fossology.org/
- QMSTR (Quartermaster), toolchain and reports – it was stalled, now back to progress, https://qmstr.org/
- Scancode-Toolkit, https://github.com/nexB/scancode-toolkit
Useful commands, when in the repository folder:mvn clean install
~/scancode-toolkit<VERSION>/scancode -cl -n 10 --csv scan-out .csv ../
- The License Compliance Verifier (LCV), demonstrator based on a subset of the compatibility rules from the Open Source Automation Development Lab (OSADL) matrix, https://github.com/fasten-project/fasten/wiki/License-compliance
- SQAaaS (Software Quality Assurance as a Service), checks for the presence of a LICENSE file with an OSI-approved licence as a part of a more extensive quality analysis (however, only compliance with the OSI Open Source Definition is required), https://sqaaas.eosc-synergy.eu/
- License Maven Plugin
Licence selection tools and resources
- Choose an open-source license, excellent simple guidance on selecting various types of open-source licences, https://choosealicense.com/, permissive licences are those which do not include the Same License condition,https://choosealicense.com/licenses/
- Joinup Licensing Assistant, finds and compares software licenses, https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/collection/eupl/solution/joinup-licensing-assistant/jla-find-and-compare-software-licenses
- The Open Source Guides site provides general resources and guides for getting started with OSS [OSG]. It also includes an excellent overview of the legal aspects of using OSS, https://opensource.guide/legal/
- Creative Commons (CC) licence chooser
- License Clearance Tool (LCT) by NI4OS-Europe suggests appropriate licences for open source and open-source products, artefacts, and research results, based on manual entry of in-licences, https://lct.ni4os.eu/
- Catalogue of standardised SPDX licence codes with licence texts, https://spdx.org/licenses/
- FOSSA set of articles about licence compliance, including an article about the Microsoft Public License (Ms-PL), https://fossa.com/product/open-source-license-compliance, https://fossa.com/blog/open-source-licenses-101-microsoft-public-license-ms-pl/
- tl;drLegal, explanations and classification of OSS licences, https://tldrlegal.com/
Compliance methodology
- In GÉANT, IPR is managed by the IPR Coordinator
- OpenChain
- Start page, https://www.openchainproject.org/
- Specification, https://wiki.linuxfoundation.org/_media/openchain/openchainspec-current.pdf
- Open Source Programs Office